Table of Contents
If you’re a new marketer stepping into the exciting world of digital marketing, you’ve probably heard the term “search engines” hundreds of times. Google, Bing, Yahoo—they all seem like magic portals that instantly deliver answers to your questions. But here’s the truth: search engines aren’t magic at all. They’re advanced programs following a set of rules, algorithms, and processes to decide which content appears on the top of search results. Understanding how search engines work is not only fascinating—it’s essential if you want to master SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and drive organic traffic to your website. In this guide, we’ll break down the complex process into simple, easy-to-understand steps.

1. What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is an online tool that helps users find information by searching through billions of web pages. It works like a huge digital library that organizes content so you can easily find what you’re looking for.
Popular examples include:
- Google (the largest and most dominant)
- Bing
- Yahoo Search
- DuckDuckGo (focuses on privacy)
- Baidu (popular in China)
The primary job of a search engine is to:
- Discover new web pages.
- Understand the content on those pages.
- Rank them based on relevance and quality.
2. The Three Main Stages of How Search Engines Work
Every search engine follows three core steps:
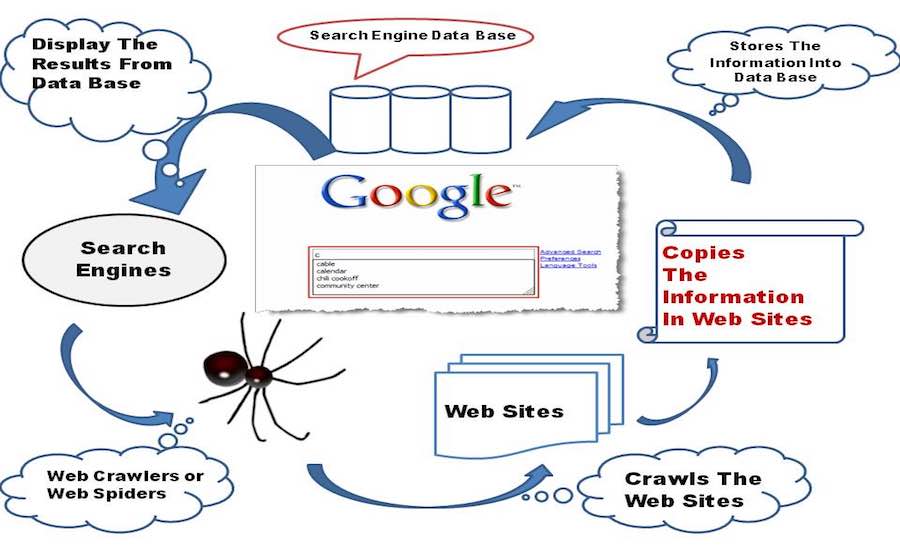
2.1 Crawling
Crawling is the process where search engines send out special bots called crawlers or spiders to discover new and updated content on the internet.
How it works:
- The crawler starts from a list of known web pages.
- It follows links from one page to another.
- It collects information about each page it visits.
Pro Tip for Marketers:
Make sure your site is crawlable by using a sitemap.xml and avoiding unnecessary blocking in your robots.txt file.
2.2 Indexing
Once a crawler finds a page, the search engine needs to understand what’s on it. This is called indexing.
During indexing, the search engine will:
- Analyze the page’s content (text, images, videos).
- Look at keywords and topics.
- Check the structure (titles, headings, meta tags).
- Store this data in its massive database (the index).
Pro Tip for Marketers:
Use relevant keywords, write clear headings, and include descriptive meta descriptions to help search engines understand your page.
2.3 Ranking
After crawling and indexing, the search engine decides where your page should appear in the search results. This is called ranking.
Ranking depends on:
- Relevance to the search query.
- Quality of the content.
- User experience (mobile-friendliness, speed).
- Backlinks from other trusted websites.
Pro Tip for Marketers:
Focus on content quality and link building to improve your rankings.
3. The Role of Algorithms in Search Engines
Search engines use complex algorithms—sets of rules—to decide which pages show up for a search.
Google’s algorithm looks at factors like:
- Keyword relevance.
- Page speed.
- Mobile-friendliness.
- Domain authority.
- User engagement (time on page, click-through rate).
Example:
If you search for “best coffee shops near me,” the algorithm will prioritize local results, customer reviews, and businesses with accurate location data.
4. Key Ranking Factors Every New Marketer Should Know
To rank higher, you need to understand what search engines value most.
4.1 On-Page SEO Factors
- Title Tags with target keywords.
- Meta Descriptions that attract clicks.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3) for structure.
- Keyword Placement in the first 100 words.
- Image Optimization with alt text.
4.2 Off-Page SEO Factors
- Backlinks from authoritative websites.
- Brand Mentions on social media.
- Guest Posting on related blogs.
4.3 Technical SEO Factors
- Fast-loading pages.
- Secure site (HTTPS).
- Mobile-friendly design.
- Proper URL structure.

See also
- Hostinger for WordPress: Full Setup + Performance Guide
- Advanced & Technical SEO: What Is Technical SEO? A Comprehensive 2025 Checklist
- Top 10 Common SEO Mistakes New Website Owners Make
5. How Search Engines Understand User Intent
Search engines are smart enough to know what the user actually means—not just what they type. This is called search intent.
Types of Search Intent:
- Informational – The user wants to learn something.
- Example: “How to bake bread.”
- Navigational – The user is looking for a specific site.
- Example: “Facebook login.”
- Transactional – The user wants to buy something.
- Example: “Buy running shoes online.”
Pro Tip for Marketers:
Match your content to the right intent. Selling too early to someone just looking for information can hurt your conversion rates.
6. The Importance of User Experience (UX)
Google and other search engines now consider user experience as a ranking factor.
UX factors include:
- Mobile-friendliness – Over 60% of searches happen on mobile.
- Page speed – Slow pages lose visitors quickly.
- Easy navigation – Users should find what they need fast.
- No intrusive pop-ups – Avoid frustrating users.
7. Common Myths About Search Engines
Myth 1: Keywords Alone Will Get You Ranked
Reality: Keywords help, but without quality content and backlinks, you won’t rank high.
Myth 2: More Pages = Higher Rankings
Reality: Quality beats quantity. Ten excellent pages will outperform 100 low-quality ones.
Myth 3: Paid Ads Improve Organic Ranking
Reality: Paid ads (PPC) don’t directly influence organic rankings.
8. Tools to Help You Understand and Work With Search Engines
Here are essential tools for marketers:
- Google Search Console – See how Google views your site.
- Google Analytics – Track user behavior.
- Ahrefs / SEMrush – Keyword and backlink research.
- Yoast SEO (WordPress) – Optimize your content easily.
9. How to Make Search Engines Love Your Website
- Create Valuable Content – Answer user questions better than anyone else.
- Optimize for Speed – Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Get Quality Backlinks – Build relationships in your niche.
- Keep Your Site Updated – Fresh content gets crawled more often.
10. The Future of Search Engines
Search engines are becoming more AI-driven, meaning they’re better at understanding natural language, context, and even images.
Trends to watch:
- Voice search optimization.
- Visual search using images.
- AI-generated summaries in search results.

Conclusion
Search engines may seem complicated, but at their core, they follow a simple process: crawl, index, and rank. As a new marketer, understanding these basics will help you create better strategies, attract more organic traffic, and build a strong online presence.
Remember, the goal is not to “trick” search engines but to work with them by creating high-quality, relevant, and user-focused content.